Netconf 学习笔记 1. Netconf简介 随着SDN的大热,一个诞生了十年之久的协议焕发了第二春,它就是NETCONF协议。如果你在两年前去搜索NETCONF协议,基本得到的信息都是“这个协议是一个网管协议,主要目的是弥补SNMP协议的不足,希望可以取代SNMP协议”。SNMP有哪些不足,而NETCONF是否真的能够弥补,这都不是重点,重点是NETCONF诞生至今SNMP依旧活的好好的。所以如果我们还是把NETCONF当做一个网管协议的话,估计它会在冷板凳上一直坐下去,而如果我们换一个角度去看待NETCONF协议,你会发现也许它是最适合SDN的一个协议。
NETCONF的自动化配置系统采用Client/Server架构,而netopeer即实现了netconf的C/S框架的开源项目。
Netopeer是基于开源项目libnetconf库完成的,已实现client和server端的代码。主要涉及的组件为netopeer-cli和netopeer-server;其中netopeer-cli为一个CLI程序,允许通过该程序连接到netconfserver,和操纵它的配置数据;netopeer-server为一个netconf服务器端的守护进程,允许与netconf client建立连接,接收配置数据等操作。除了这两个重要的模块,netopeer项目还包含了libnetconf transAPI模块举例,位于项目源码transAPI/路径下,例如cfgsystem模块,实现的是一个ietf-system数据模型。
2. Netconf架构 NETCONF是一个基于XML的交换机配置接口,用于替代CLI、SNMP等配置交换机。
本质上来说,NETCONF就是利用XML-RPC的通讯机制实现配置客户端和配置服务端之间的通信,实现对网络设备的配置和管理。
NETCONF分为四个层:安全传输层、消息层、操作层、内容层。
安全传输层 :用于跟交换机安全通信,NETCONF并未规定具体使用哪种传输层协议,所以可以使用SSH、TLS、HTTP等各种协议
消息层 :提供一种传输无关的消息封装格式,用于RPC通信
操作层 :定义了一系列的RPC调用方法,并可以通过Capabilities来扩展
内容层 :定义RPC调用的数据内容
NETCONF关键技术实现:
关键的环节包括:安全认证、建立加密传输通道、rpc-xml消息收发、rpc-xml文件解析、rpc-reply消息的生成。
3. Netconf环境搭建 基于centos7搭建环境:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ sudo yum install libtool $ sudo yum install libxml2-devel $ sudo yum install libxslt-devel $ sudo yum install libcurl-devel $ sudo yum install python-setuptools $ sudo yum install pkg-config $ sudo yum install readline-devel
pyang 编译安装 1 2 3 $ git clone https://github.com/mbj4668/pyang.git $ cd pyang$ python setup.py install
libssh (>=0.6.4) 编译安装 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $ sudo yum install libssh-devel # or $ git clone https://git.libssh.org/projects/libssh.git libssh $ cd libssh$ mkdir build$ cd build$ cmake .. $ make $ sudo make install $ cd ..
libnetconf 编译安装 1 2 3 4 5 $ git clone https://github.com/CESNET/libnetconf.git $ cd libnetconf$ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install
netopeeran编译安装 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 $ git clone https://github.com/CESNET/netopeer.git # 编译安装netopeer-server $ cd netopeer/server$ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install # 编译安装netopeer-cli $ cd netopeer/cli$ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install
netopeer 启动与验证 启动netopeer server
1 2 $ netopeer-server -d # 默认监听端口x.x.x.x:830,连接的用户名密码为系统用户
验证 netopeer-cli 与 netopeer-server 连接
1 2 3 $ netopeer-cli netconf> connect localhost netconf> get-config startup
其它操作
1 2 3 4 5 # a) 配置netopeer server模块 $ netopeer-configurator # b) 检查默认启动的模块 $ netopeer-manager list
4. Netconf案例使用 假设经过第一步后成功编译出libnetconf和netopeer,这样我们就可以直接运行netopeer。netconf默认监听端口是830端口。
众所周知,netconf协议支持自定义rpc,因此此步骤需要做的是如何在现有netconf中增加自己的yang模型以及执行自己的rpc??
这里就需要用到这个工 lnctool。这个工具是用python实现的,里面代码也比较简单,比如说调用其他应用程序(pyang)或者直接写文件。
1 $ lnctool --model ./turing-machine.yang transapi --paths ./path
另外一个重点是就是实现源文件中相关接口—rpc函数。当经过以上两个步骤之后,就可以进行编译,默认编译出动态库.so文件。
当我们把rpc函数实现之后,就可以通过另外一个工具,netopeer-manager安装自定义模型,使用命令行如下:
1 2 3 $ netopeer-manager add --name [module name] --model [model path] --transapi [model share library] --datastore [module datastore file] $ netopeer-manager add --name turing-machine --model /usr/local/etc/netopeer/turing-machine/turing-machine.yin --transapi /usr/local/lib/turing-machine.so --datastore /usr/local/etc/netopeer/turing-machine/datastore.xml
turing-machine demo 1. 编译 turing-machine 1 2 3 $ autoreconf --force --install $ ./configure $ make
2. 检查 xml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 $ cat /usr/local/etc/netopeer/cfgnetopeer/datastore.xml<?xml version="1.0"?> <datastores xmlns="urn:cesnet:tmc:datastores:file"> <running lock=""> <netopeer xmlns="urn:cesnet:tmc:netopeer:1.0"> <modules> <module> <name>turing-machine</name> <enabled>true</enabled> </module> </modules> </netopeer> </running> <startup lock=""> <netopeer xmlns="urn:cesnet:tmc:netopeer:1.0"> <modules> <module> <name>turing-machine</name> <enabled>true</enabled> </module> </modules> </netopeer> </startup> <candidate lock="" modified="false" locktime=""> <netopeer xmlns="urn:cesnet:tmc:netopeer:1.0"> <modules> <module> <name>turing-machine</name> <enabled>true</enabled> </module> </modules> </netopeer> </candidate> </datastores> $ cat /usr/local/etc/netopeer/cfgnetopeer/datastore-server.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <datastores xmlns="urn:cesnet:tmc:datastores:file"> <running lock=""/> <startup lock=""/> <candidate modified="false" lock="" locktime=""/> </datastores>
3. 安装模块 1 2 3 4 5 $ su root $ cp turing-machine.yin /usr/local/etc/netopeer/turing-machine/$ cp .libs/turing-machine.so /usr/local/lib$ cp turing-machine.la /usr/local/lib$ netopeer-manager add --name turing-machine --model /usr/local/etc/netopeer/turing-machine/turing-machine.yin --transapi /usr/local/lib/turing-machine.so --datastore /usr/local/etc/netopeer/turing-machine/datastore.xml
4. netopeer-manager list 1 2 3 4 $ netopeer-manager list Reading the configuration from /usr/local/etc/netopeer/modules.conf.d/ List of startup Netopeer modules: turing-machine (enabled)
5. 启动 netopeer-server 1 2 $ netopeer-server -v 3 ...
6. 启动 netopeer-cli 使用命令:
connect 192.168.205.98
get
lock candidate
edit-config candidate
commit
unlock candidate
get-config running Get-config
edit-config candidate
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 $ netopeer-cli netconf> connect 192.168.205.98 The authenticity of the host '192.168.205.98' cannot be established. ssh-rsa key fingerprint is 9f:c8:f9:13:7d:04:b8:18:e9:4d:4e:9c:cb:63:84:17:0b:d9:ad:6a. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes root@192.168.205.98 password: netconf> get ...... netconf> lock candidate Result OK netconf> debug Verbose level set to DEBUG netconf> edit-config --defop=merge --config=/root/turing.xml candidate libnetconf DEBUG: 4984-D 1-26 14:34:38 Writing message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="3"> <edit-config> <target> <candidate/> </target> <default-operation>merge</default-operation> <config> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine" xmlns:xc="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <transition-function xc:operation="merge"> <delta> <label>0</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </output> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </config> </edit-config> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: 4984-D 1-26 14:34:38 11--Received message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="3"> <ok/> </rpc-reply> Result OK netconf> commit libnetconf DEBUG: 4984-D 1-26 14:35: 9 Writing message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="4"> <commit/> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: 4984-D 1-26 14:35: 9 11--Received message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="4"> <ok/> </rpc-reply> Result OK
7. check datastore.xml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 $ cat /usr/local/etc/netopeer/turing-machine/datastore.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <datastores xmlns="urn:cesnet:tmc:datastores:file"> <running lock=""> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <transition-function> <delta> <label>0</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </output> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </running> <startup lock=""/> <candidate modified="true" lock="1" locktime="2018-01-26T06:33:55Z"> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <transition-function> <delta> <label>0</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </output> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </candidate> </datastores>
OK, unlock candidate:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 netconf> unlock candidate libnetconf DEBUG: 4984-D 1-26 14:38: 4 Writing message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="5"> <unlock> <target> <candidate/> </target> </unlock> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: 4984-D 1-26 14:38: 4 11--Received message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="5"> <ok/> </rpc-reply> Result OK netconf>
unlock is successfully
server’s output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 netopeer-server[4981]: 4981-D 1-26 14:38: 4 11--Received message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="5"> <unlock> <target> <candidate/> </target> </unlock> </rpc> netopeer-server[4981]: 4981-V 1-26 14:38: 4 Created dummy session 0 for user 'root' (UID 0) - recovery session netopeer-server[4981]: 4981-V 1-26 14:38: 4 Created dummy session 0 for user 'root' (UID 0) - recovery session netopeer-server[4981]: 4981-D 1-26 14:38: 4 Adding new event (0) netopeer-server[4981]: 4981-V 1-26 14:38: 4 Created dummy session 0 for user 'root' (UID 0) - recovery session netopeer-server[4981]: 4981-D 1-26 14:38: 4 Writing message (session 1): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="5"> <ok/> </rpc-reply>
turing-machine demo get操作案例 running datestore 内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 netconf> get-config running Result: <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <transition-function > <delta > <label > 0</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </output > </delta > <delta > <label > 1</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </output > </delta > <delta > <label > end</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol /> </input > <output > <state > 1</state > </output > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine > <netopeer xmlns ="urn:cesnet:tmc:netopeer:1.0" > <modules > <module > <name > turing-machine</name > <enabled > true</enabled > </module > </modules > </netopeer > netconf>
准备get xml文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <transition-function > <delta > <label > 0</label > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
netopeer-cli 命令:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 netconf> get --filter=/turing-machine-get-test.xml Result: <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <transition-function > <delta > <label > 0</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </output > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
netopeer-server log:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 netopeer-server[127219]: Received message (session 4): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <rpc xmlns ="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id ="34" > <get > <filter type ="subtree" > <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <transition-function > <delta > <label > 0</label > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine > </filter > </get > </rpc > netopeer-server[127219]: Merging the node turing-machine (src/datastore/edit_config.c:2325) netopeer-server[127219]: Deleting the node turing-machine (src/datastore/edit_config.c:1003) netopeer-server[127219]: Writing message (session 4): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <rpc-reply xmlns ="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id ="34" > <data > <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <transition-function > <delta > <label > 0</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </output > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine > </data > </rpc-reply >
配置netopeer服务器模块 要查找要添加YANG模块的默认位置,请运行
1 $ sudo /usr/bin/netopeer-configurator
你可以在[Netopeer]一栏找到以下信息
1 [Netopeer] Using modules installed in path: /usr/local/etc/netopeer/modules.conf.d
默认情况下,所有模块的XML实例数据(Netopeer调用这个数据存储,不幸的是,使用与NETCONF的运行/候选/启动数据存储相同的术语)存储在 /usr/local/etc/Netopeer/modules.conf.d中
当您使用 netopier -manager 添加模块时,—datastore 选项应该指向 /usr/local/etc/netopeer/modules.conf.d
使用 netopier -manager 的例子:
首先检查哪些模块是默认启用的:
1 2 $ netopeer-manager list List of startup Netopeer modules:No module installed.
没有安装模块。让我们添加一些模块。要添加模型,首先使用PyangNETCONFc转换 .yang 文件 yin文件。Netopeer内部使用 YIN 格式。例如,让我们添加 toaster 数据存储,这样您就可以使用NETCONFc来配置它。
Download toaster.yang from http://seguesoft.com/get-standard-yang-modules . Then you can do:
1 $ pyang -f yin /home/bob/YANG_modules/toaster.yang -o /home/bob/YANG_modules/toaster.yin
Then add toaster.yin’s datastore into Netopeer as follows
1 $ netopeer-manager add --name toaster --model /home/bob/YANG_modules/toaster.yin --datastore /usr/local/etc/netopeer/modules.conf.d/toaster.xml
对于命令引用类型
1 2 $ netopeer-manager add --help To actually implement a model, see http://github.com/CESNET/netopeer/tree/master/transAPI/cfgsystem
操作过程: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 # xml 生成 $ pyang -f sample-xml-skeleton turing-machine.yang -o turing-machine.xml # 生成 rpc 接口代码 $ lnctool --model ./turing-machine.yang transapi --paths ./path # netconf log 接口 nc_verb_verbose("Miaow: Turing machine transapi_init..."); # 编译 rpc 模块代码,并安装模块 $ autoreconf --force --install $ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install # 查看已安装的模块 $ netopeer-manager list $ man netopeer-manager
启动服务测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 $ sudo /usr/local/bin/netopeer-server -v 3 $ sudo /usr/local/bin/netopeer-cli netconf> help # Available commands: # help Display this text # connect Connect to a NETCONF server # listen Listen for a NETCONF Call Home # disconnect Disconnect from a NETCONF server # commit NETCONF <commit> operation # copy-config NETCONF <copy-config> operation # delete-config NETCONF <delete-config> operation # discard-changes NETCONF <discard-changes> operation # edit-config NETCONF <edit-config> operation # get NETCONF <get> operation # get-config NETCONF <get-config> operation # get-schema NETCONF <get-schema> operation # kill-session NETCONF <kill-session> operation # lock NETCONF <lock> operation # unlock NETCONF <unlock> operation # validate NETCONF <validate> operation # test Run a specified test case # subscribe NETCONF Event Notifications <create-subscription> operation # time Enable/disable measuring time of command execution # knownhosts Manage known hosts in the "~/.ssh/known_hosts" file # status Print information about the current NETCONF session # user-rpc Send your own content in an RPC envelope (for DEBUG purposes) # verbose Enable/disable verbose messages # quit Quit the program # auth Manage SSH authentication options # capability Add/remove capability to/from the list of supported capabilities # editor Manage the editor to be used for manual XML pasting/writing netconf> connect 127.0.0.1 netconf> get -h # get [--help ] [--defaults report-all|report-all-tagged|trim|explicit] [--filter [file]] [--out file] netconf> get --filter=/root/turing.xml netconf> get-config -h # get-config [--help ] [--defaults report-all|report-all-tagged|trim|explicit] [--filter [file]] [--out file] running|startup|candidate netconf> get-config --filter=/root/turing.xml candidate netconf> edit-config -h # edit-config [--help ] [--defop <merge|replace|none>] [--error <stop|continue |rollback>] [--test <set |test-only|test-then-set>] [--config <file> | --url <url>] running|startup|candidate # If neither --config nor --url is specified, user is prompted to set edit data manually. netconf> lock candidate netconf> debug netconf> edit-config --defop=merge --config=/root/turing.xml candidate netconf> commit netconf> unlock candidate netconf> netconf> user-rpc --file=/root/rpc-run.xml
5. turing-machine 操作层示例 安装好 turing-machine 之后,可以对模块做一些操作,以下为实际的操作过程以及对应的xml编写示例。
<edit-config> 详解:
描述:
操作将全部或部分指定配置加载到指定的目标配置数据存储。此操作允许以多种方式表示新配置,例如使用本地文件,远程文件或内联。如果目标配置数据存储不存在,它将被创建。
如果一个NETCONF节点(peer)支持:url能力(8.8节 ),那么元素可以出现而不是参数。
设备分析源和目标配置并执行所请求的更改。目标配置不一定被替换,就像``消息一样。而是根据源数据和请求的操作来更改目标配置。
如果操作包含应用于基础数据模型中相同概念节点的多个子操作,则操作的结果是未定义的(即,不在NETCONF协议的范围之内)。
属性:
operation:子树中的元素可以包含一个“`operation`”属性,它属于[3.1](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6241#section-3.1)节定义的`NETCONF`名称空间。该属性标识配置中的要执行该操作的点,并可以在整个子树中的多个元素上出现。如果未指定“operation”属性,则配置将合并到配置数据存储中。 “operation”属性具有以下值之一:
merge:由包含此属性的元素标识的配置数据与由``参数标识的配置数据存储中对应级别的配置合并。这是默认行为。replace:由包含此属性的元素标识的配置数据将替换由参数标识的配置数据存储区中的任何相关配置。如果配置数据存储中不存在此类配置数据,则会创建它。与替换整个目标配置的操作不同,只有实际存在于``参数中的配置受到影响。create:当且仅当配置数据存在于配置数据存储中时,才将包含此属性的元素标识的配置数据添加到配置中。如果配置数据存在,则返回一个值为“`data-exists`”的元素。delete:当且仅当配置数据当前存在于配置数据存储中时,才从配置中删除由包含此属性的元素标识的配置数据。如果配置数据不存在,则返回一个值为“`data-missing`”的元素。remove:如果配置数据当前存在于配置数据存储中,则从配置中删除由包含此属性的元素标识的配置数据。如果配置数据不存在,服务器会自动忽略“remove”操作。
参数:
target:正在编辑的配置数据存储的名称,例如或。default-operation:选择此请求的默认操作(如“`operation`”属性中所述)。 参数的默认值是“merge”。参数是可选的,但是如果提供,它具有以下值之一:
merge:参数中的配置数据与目标数据存储中相应级别的配置合并。这是默认行为。replace:参数中的配置数据完全替换了目标数据存储中的配置。这对加载以前保存的配置数据很有用。none:目标数据存储不受参数中的配置影响,除非和直到传入的配置数据使用“`operation`”属性请求不同的操作。如果参数中的配置包含目标数据存储中没有相应级别的数据,则返回,并带有缺少数据的值。使用“none”允许像“delete”这样的操作避免无意中创建要删除的元素的父层次结构。
test-option:只有当设备公布支持:validate:1.1能力时才能指定元素([8.6节](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6241#section-8.6))。元素具有以下值之一:
test-then-set:在尝试设置之前执行验证测试。 如果发生验证错误,请不要执行``操作。 这是默认的测试选项。set:先执行一个没有验证测试的设置。test-only:仅执行验证测试,而不尝试设置。
error-option:元素具有以下值之一:
stop-on-error:停止第一个错误的``操作。这是默认的错误选项。continue-on-error:继续处理错误的配置数据;记录错误,如果发生任何错误,则产生否定响应。rollback-on-error:如果发生错误情况,从而生成错误严重性元素,则服务器将停止处理操作,并在指定的开始时将指定的配置恢复到完整状态这个``操作。该选项要求服务器支持8.5节 中描述的错误回滚功能。
config:配置数据的层次结构,由设备的一个数据模型定义。内容必须放置在适当的命名空间中,以允许设备检测适当的数据模型,并且内容必须遵循该数据模型的约束,如其能力定义所定义。能力在第8节 讨论。
创建实例 turing.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <transition-function > <delta > <label > 0</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </output > </delta > <delta > <label > 1</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </output > </delta > <delta > <label > end</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol /> </input > <output > <state > 1</state > </output > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
为 turing-machine 创建实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 netconf> edit-config --defop=merge --config=/root/turing.xml candidate libnetconf DEBUG: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="8"> <edit-config> <target> <candidate/> </target> <default-operation>merge</default-operation> <config> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <transition-function> <delta> <label>0</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </output> </delta> <delta> <label>1</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </output> </delta> <delta> <label>end</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol/> </input> <output> <state>1</state> </output> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </config> </edit-config> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="8"> <ok/> </rpc-reply>
删除数据 delete-delta.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" xmlns:xc ="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" > <transition-function > <delta xc:operation ="remove" > <label > 1</label > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
删除 delta 中的一项:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 netconf> edit-config --defop=none --config=/root/delete-delta.xml candidate libnetconf DEBUG: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="13"> <edit-config> <target> <candidate/> </target> <default-operation>none</default-operation> <config> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine" xmlns:xc="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"> <transition-function> <delta xc:operation="remove"> <label>1</label> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </config> </edit-config> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="13"> <ok/> </rpc-reply> netconf> get-config candidate libnetconf DEBUG: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="14"> <get-config> <source> <candidate/> </source> </get-config> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="14"> <data> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <transition-function> <delta> <label>0</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </output> </delta> <delta> <label>end</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol/> </input> <output> <state>1</state> </output> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </data> </rpc-reply>
创建数据 create-delta.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" xmlns:xc ="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" > <transition-function > <delta xc:operation ="create" > <label > 3</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 1</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </output > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
创建 delta 数据:
1 netconf> edit-config --defop=none --config=/root/create-delta.xml candidate
合并和替换数据 merge-delta.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" xmlns:xc ="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" > <transition-function > <delta xc:operation ="merge" > <label > 0</label > <input > <state > 1</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 1</state > <symbol > 1</symbol > </output > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
replace-delta.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" xmlns:xc ="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" > <transition-function > <delta xc:operation ="replace" > <label > 3</label > <input > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </input > <output > <state > 0</state > <symbol > 0</symbol > </output > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
合并和替换 delta:
1 2 netconf> edit-config --defop=none --config=/root/merge-delta.xml candidate netconf> edit-config --defop=none --config=/root/replace-delta.xml candidate
获取数据 get-turing.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > </turing-machine >
get-delta-0.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <turing-machine xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <transition-function > <delta > <label > 0</label > </delta > </transition-function > </turing-machine >
获取特定数据:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 netconf> get --filter=/root/get-turing.xml libnetconf DEBUG: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="17"> <get> <filter type="subtree"> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> </turing-machine> </filter> </get> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="17"> <data> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <transition-function> <delta> <label>0</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </output> </delta> <delta> <label>1</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </output> </delta> <delta> <label>end</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol/> </input> <output> <state>1</state> </output> </delta> </transition-function> <state>0</state> <head-position>0</head-position> <tape> <cell> <coord>0</coord> <symbol>0</symbol> </cell> </tape> </turing-machine> </data> </rpc-reply> netconf> get --filter=/root/get-delta-0.xml libnetconf DEBUG: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="18"> <get> <filter type="subtree"> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <transition-function> <delta> <label>0</label> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </filter> </get> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="18"> <data> <turing-machine xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <transition-function> <delta> <label>0</label> <input> <state>0</state> <symbol>0</symbol> </input> <output> <state>0</state> <symbol>1</symbol> </output> </delta> </transition-function> </turing-machine> </data> </rpc-reply>
自定义 rpc 方法调用 rpc-initialize.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 4 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <initialize xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > <tape-content > 0</tape-content > </initialize >
执行 rpc-initialize :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 netconf> user-rpc --file=/root/rpc-initialize.xml libnetconf DEBUG: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="19"> <initialize xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <tape-content>0</tape-content> </initialize> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="19"> <ok/> </rpc-reply>
server 响应内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 netopeer-server[14444]: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="20"> <initialize xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> <tape-content>0</tape-content> </initialize> </rpc> netopeer-server[14444]: Calling initialize RPC function netopeer-server[14444]: Miaow: Turing machine rpc_initialize... netopeer-server[14444]: Miaow: Turing machine get_rpc_node... netopeer-server[14444]: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="20"> <ok/> </rpc-reply>
rpc-run.xml 内容如下:
1 2 3 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <run xmlns ="http://example.net/turing-machine" > </run >
执行 rpc-run :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 netconf> user-rpc --file=/root/rpc-run.xml libnetconf DEBUG: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="21"> <run xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> </run> </rpc> libnetconf DEBUG: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="21"> <ok/> </rpc-reply>
server 响应内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 netopeer-server[14444]: Received message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="21"> <run xmlns="http://example.net/turing-machine"> </run> </rpc> netopeer-server[14444]: Calling run RPC function netopeer-server[14444]: Miaow: Turing machine rpc_run... netopeer-server[14444]: Writing message (session 7): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <rpc-reply xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0" message-id="21"> <ok/> </rpc-reply> netopeer-server[14444]: Adding new event (0)
notification 测试 TODO
6. Netconf总结 Netconf2
TODO
Netconf 2 使用介绍 pyang 工具使用 yang建模语言及pyang背景简介
YANG(RFC 7950)是NETCONF(RFC 6241)的数据建模语言,由IETF NETMOD WG开发。
pyang是一个YANG验证器,转换器和代码生成器,用python编写。 它可用于验证YANG模块的正确性,将YANG模块转换为其他格式,以及从模块生成代码。
sdn、nfv盛行的今天,yang建模语言变得越来越重要,它定义于netconf协议,但是却超越了netconf协议本身,在网络世界迸发自己的活力。
如今最大的开源sdn控制器-opendaylight以yang作为建模语言进行核心模型存储,netconf以及restconf纷纷依靠yang模型定义接口,定义南向模型、北向模型。最具sdn气息的openflow也有个伴侣协议of-config使用yang建模,借助netconf通道下发相关配置。
yang很重要,但是用好yang可以选择的工具却并不多,pyang就是其中很重要的一个,这是一个由python代码编写的yang语法验证器、转换器以及代码生成器,一些开源软件使用它构建模型校验语法,比如开源netconf agent netopeer,我们作为用户也可以使用它进行语法校验,生成tree、yin等其它格式模型、数据。它是一个命令行,是一个学习好yang之路的一个好用的工具。
pyang工具特性
Validate YANG modules. 校验yang模型;
Convert YANG modules to YIN, and YIN to YANG. yang和yin模型相互转换
Translate YANG data models to DSDL schemas, which can be used for validating various XML instance documents. See InstanceValidation . yang模型与dsdl结构模型转化
Translate YANG data models to XSD. yang与xsd转化;
Generate UML diagrams from YANG models. See UMLOutput for an example. 生成yang模型uml;
Generate compact tree representation of YANG models for quick visualization. See TreeOutput for an example. 生成tree来呈现yang的快速视图;
Generate a skeleton XML instance document from the data model. 生成xml骨架实例;
Schema-aware translation of instance documents encoded in XML to JSON and vice-versa. See XmlJson . xml、json实例转换
Plugin framework for simple development of other outputs, such as code generation. 其他开发输出的框架插件,例如代码生成;
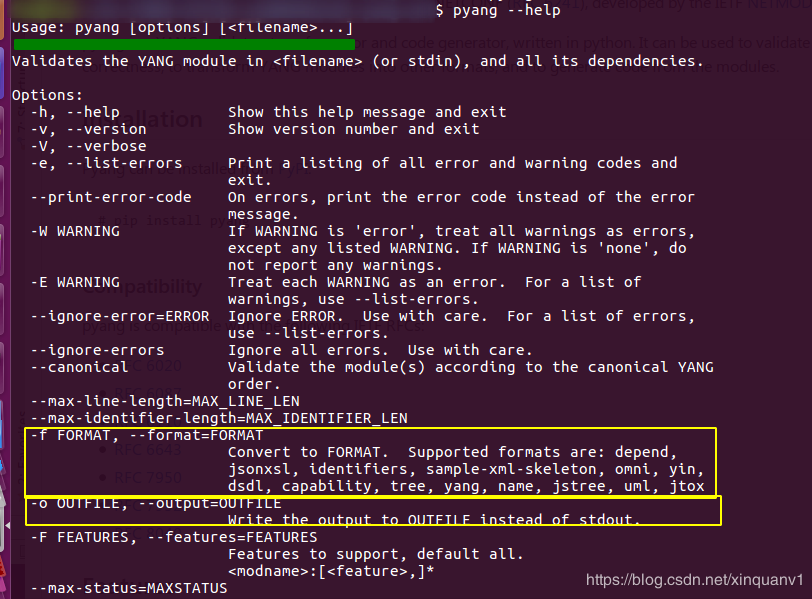
pyang 命令行简介 pyang命令行的使用,提供了丰富的文档说明通过pyang –help或者man pyang都能看到非常详细的信息:
普通用户模式转换主要关注如下几个即可:
-f 输出格式,这里支持的格式包括tree、yang、yin等,用户可以根据需求灵活选择;
-o 输出文件名;
-p 输出路径;
pyang 的yin、yang 模型转化 pyang的格式 yin和yang转换很简单,按照下面命令完成即可:
1 $ pyang -f yin -o ietf-yang-types.yin ietf-yang-types.yang
pyang 生成 tree 文件 tree 文件是 yang 独有的一个文件,主要功能就是为 yang 生成一个快速化的浏览视图.
如下所示为一个批量处理 yang 文件生成 tree 文件的命令行:
1 $ pyang -f tree yangdir/*.yang -o ouputdir/output.tree
yang 语法校验 因为没有仔细理解功能,这里只是将功能简单尝试了以下,后续有机会再系统的梳理一下这个功能,此处只给出简单的说明:
1 $ pyang --ietf test.yang
pyang 小结 总的来说pyang是我们使用yang的一个必不可少的命令行、工具和插件,这里给出的一只是笔者平时的一些使用经验,它还有许多强大的功能在这里没有一一详述。
yang-explorer, 一个开源的杨浏览器和 RPC Builder
yang-explorer, 一个开源的杨浏览器和 RPC Builder
An open-source Yang Browser and RPC Builder Application
Git URL:
1 $ git://www.github.com/CiscoDevNet/yang-explorer.git
Git Clone代码到本地:
1 $ git clone http://www.github.com/CiscoDevNet/yang-explorer
Subversion代码到本地:
1 2 3 4 $ svn co --depth empty http://www.github.com/CiscoDevNet/yang-explorer Checked out revision 1. $ cd repo$ svn up trunk
描述开源Yang浏览器和 RPC Builder应用Yang数据模型实验 功能
从用户界面或者 命令行 上传/编译yang模型
生成 NetConf RPC
生成 python 示例代码 [new]
搜索 yang [new]
针对真正的netconf服务器执行 RPC
将创建的rpc保存到收藏集以便以后使用
建立模型的依赖关系图
浏览数据模型树并检查杨属性
安装
1 2 3 If already installed, make sure that pip/setuptools are upto date (commands may vary) pip install --upgrade pip Ubuntu: sudo pip install --upgrade setuptools
1 2 3 Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install python-virtualenv Fedora: sudo dnf install python-virtualenv MAC: sudo pip install virtualenv
1 2 3 Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install graphviz Fedora: sudo dnf install graphviz MAC: brew install graphviz
带有最新 Flash 插件的浏览器( 通过 Google Chrome 测试)
Download 和 安装:
1 2 3 4 $ git clone https://github.com/CiscoDevNet/yang-explorer.git $ cd yang-explorer$ bash setup.sh # Note: sudo may be required if you do not use virtualenv.
有关更多信息,请参见第 7节疑难解答:
1 2 3 4 If you get installation error for missing python.h or xmlversion.h try installing dependency packages: Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev python-dev zlib1g-dev Fedora: sudo dnf install libxml2-devel libxslt-devel python-devel zlib-devel
更新 exising 安装
1 2 3 4 5 $ cd <install-root>/yang-explorer$ git stash (if you have local changes) $ git pull origin $ git stash apply (if you have local changes) $ bash setup.sh
备份数据
可以从数据目录备份YangExplorer数据,并且可以移植到新服务器上。
1 $ cp -r <install-root>/yang-explorer/server/data <backup-location>/data
从备份位置还原
1 2 3 $ cd <install-root>/yang-explorer/server# move current data to tmp location mv data data_old # replace data from backup location cp -r <backup-location>/data data
运行 YangExplorer, localhost Start 服务器:
1 2 3 $ cd <install-root>/yang-explorer$ [sudo]./start.sh & # Note: sudo may be required if you did not use virtualenv during installation.
Start 资源管理器:
1 http://localhost:8088/static/YangExplorer.html
运行 ip 地址( 共享服务器) Start 服务器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 # Determine <ip-address> using if-config $ vi YangExplorer.html var flashvars = {}; + flashvars.host = '<ip-address>';+ flashvars.port = '8088'; # save & quit $ vi start.sh (update HOST variable with <ip-address>) # save & quit. /start.sh # Note: sudo may be required if you did not use virtualenv during installation.
Start 资源管理器:
1 http://<ip-address>:8088/static/YangExplorer.html
virtual python env
创建 virtual python env
python环境神器virtualenvwrapper安装与使用
Reference 模块下载地址
模块编译安装
NETCONF协议netopeer软件安装与环境搭建
Set up Netopeer Server to use with NETCONFc
NETCONF协议之netopeer软件安装
netconf学习资料
软件定义网络基础—NETCONF协议
Netconf配置及其RPC和Notification下发流程解析
NETCONF协议详解
NETCONF模块设计介绍
netopeer工具的使用
【开源推介02-pyang】-你离yang模型只差一个pyang工具
netconf相关问题解决
An error occurred after executing the ‘commit‘’ command
cannot execute lock/unlock from netopeer-cli
YANG Tools:Yang1.1 Draft Yang Tools: Yang1.1 Draft
edit-config with delete=”operation” not working
其他
关于RFC6241中文翻译
YANG 1.1 数据建模语言
网络基础
NETCONF Support for Event Notifications
Custom Subscription to Event Streams
YANG模型介绍及语法
SDN实战团分享(七):YANG模型与OpenDaylight南北向接口
深入浅出理解 YANG 模型
配置NETCONF/YANG并且验证Cisco IOS XE 16.x平台的示例
Yang解析
CloudEngine 7800&6800&5800 V100R003C00 配置指南-网络管理与监控配置
NE20E-S2 V800R010C10SPC500 配置指南 - 系统管理 01
NETCONF 学习 – python